Which of the following is true regarding metabolic pathways? This question delves into the intricate world of cellular processes, where chemical reactions orchestrate the very essence of life. Metabolic pathways, the focus of this discourse, are the intricate networks that govern these reactions, shaping cellular function and ultimately dictating the health and vitality of organisms.
From the bustling streets of glycolysis to the powerhouses of the Krebs cycle, metabolic pathways orchestrate a symphony of chemical transformations, extracting energy from nutrients, synthesizing essential molecules, and eliminating waste products. Their significance extends far beyond the confines of individual cells, influencing whole-body physiology, shaping development, and even contributing to the onset of disease.
1. Metabolic Pathways Overview
Metabolic pathways are interconnected series of chemical reactions that occur within cells. They are essential for the conversion of nutrients into energy and the synthesis of new molecules.
There are two main types of metabolic pathways: catabolic pathways and anabolic pathways. Catabolic pathways break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. Anabolic pathways use energy to build more complex molecules from simpler ones.
Some of the most common metabolic pathways include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. These pathways are responsible for generating energy for the cell.
2. Characteristics of Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways have several general characteristics. First, they are typically catalyzed by enzymes. Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions.
Second, metabolic pathways are regulated. This regulation ensures that the pathways only occur when they are needed and that the products of the pathways are not overproduced.
Finally, metabolic pathways are often interconnected. This means that the products of one pathway can be used as the substrates for another pathway.
3. Interconnectedness of Metabolic Pathways
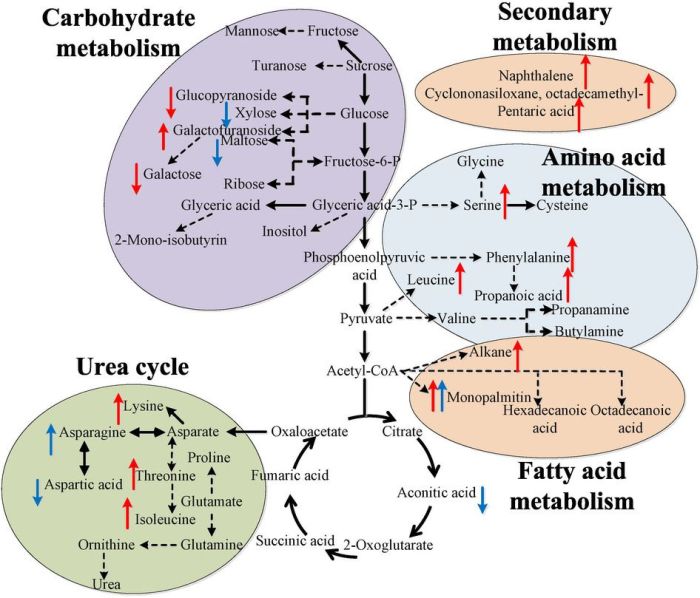
Metabolic pathways are interconnected in a complex network. This network allows cells to efficiently convert nutrients into energy and to synthesize new molecules.
One example of interconnected metabolic pathways is the glycolysis pathway and the citric acid cycle. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate. Pyruvate can then be used to enter the citric acid cycle, which generates energy for the cell.
4. Importance of Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways are essential for cellular function. They provide the cell with energy and the building blocks it needs to synthesize new molecules.
One of the most important metabolic pathways is the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain generates energy for the cell by transferring electrons from one molecule to another.
Metabolic pathways are also essential for the synthesis of new molecules. For example, the citric acid cycle is used to synthesize amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
5. Disorders of Metabolic Pathways

Disorders of metabolic pathways can lead to a variety of diseases. These diseases can be caused by genetic defects, environmental factors, or a combination of both.
One example of a disorder of metabolic pathways is phenylketonuria (PKU). PKU is caused by a genetic defect that prevents the body from breaking down the amino acid phenylalanine. This can lead to intellectual disability and other health problems.
There are a variety of treatments for disorders of metabolic pathways. These treatments can include dietary changes, medication, and enzyme replacement therapy.
6. Emerging Research in Metabolic Pathways
There is a great deal of ongoing research on metabolic pathways. This research is focused on understanding how metabolic pathways are regulated and how they can be manipulated to treat diseases.
One area of research is focused on the development of new drugs that can target metabolic pathways. These drugs could be used to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and obesity.
Another area of research is focused on the use of genetic engineering to correct genetic defects that lead to disorders of metabolic pathways.
Expert Answers: Which Of The Following Is True Regarding Metabolic Pathways
What is the primary function of metabolic pathways?
Metabolic pathways are responsible for converting nutrients into energy and synthesizing essential molecules for cellular function.
How are metabolic pathways regulated?
Metabolic pathways are regulated by a complex interplay of enzymes, hormones, and other signaling molecules.
What are the consequences of metabolic pathway disorders?
Disorders of metabolic pathways can lead to a wide range of health problems, including diabetes, obesity, and certain types of cancer.