Embark on an enthralling journey with our APHG Unit 4 Practice Test, where you’ll delve into the fascinating world of population, migration, and urbanization. Prepare to expand your knowledge and sharpen your analytical skills as we uncover the intricacies of human geography.
Throughout this practice test, you’ll encounter real-world examples, engage in data analysis, and explore the complex dynamics that shape our planet’s population distribution and movement.
Understanding APHG Unit 4 Concepts

Unit 4 of AP Human Geography explores the intricate relationships between population, migration, and urbanization, shaping the human experience across the globe. These concepts are fundamental to understanding the distribution, growth, and movement of human populations, as well as their profound impact on societies and the environment.
Population
Population refers to the total number of individuals residing in a particular area or region. Population dynamics, including birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns, influence population growth and distribution. Factors such as economic development, healthcare access, and environmental conditions can significantly affect population trends.
Migration
Migration encompasses the movement of individuals from one place to another, whether within a country or across international borders. Migration can be driven by various factors, such as economic opportunities, political instability, environmental disasters, or family reunification. Understanding migration patterns is crucial for addressing issues related to integration, cultural exchange, and global population dynamics.
Urbanization
Urbanization refers to the process of population concentration in urban areas, resulting in the growth of cities and towns. Urbanization is driven by factors such as industrialization, economic opportunities, and technological advancements. It brings both benefits and challenges, including increased access to services and infrastructure, but also issues related to congestion, pollution, and social inequality.
Analyzing Population Data
Understanding population data is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of human societies. Population data provide valuable insights into the size, composition, and distribution of populations, which are essential for planning, policymaking, and research.
If you’re feeling a little rusty on your AP Human Geography Unit 4 material, why not take a quick break and test your knowledge of Romeo and Juliet Act 3 with this quiz ? It’s a fun way to refresh your memory and get back in the swing of things for your APHG Unit 4 practice test.
Types of Population Data and Sources
- Census data:Collected through government-conducted surveys, providing comprehensive information about a population at a specific point in time.
- Vital statistics:Records of births, deaths, and marriages, providing data on population growth and decline.
- Population estimates:Projections based on census data and vital statistics, providing estimates of population size and characteristics between census years.
- Population registers:Ongoing records of individuals, providing detailed information about their demographic characteristics and migration patterns.
Interpreting Population Pyramids and Other Graphical Representations
Population pyramids and other graphical representations of population data allow for visual analysis of population structure and dynamics.
- Population pyramids:Bar charts that display the age and sex distribution of a population, providing insights into fertility, mortality, and migration patterns.
- Cohort-component method:A technique used to estimate future population size and structure based on past trends and assumptions about fertility, mortality, and migration.
- Life tables:Tables that provide information about the probability of death at different ages, allowing for the calculation of life expectancy and other demographic measures.
Factors Influencing Population Growth and Decline
Population growth and decline are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Fertility:The average number of children born to women in a population.
- Mortality:The number of deaths in a population.
- Migration:The movement of people into and out of a population.
- Age structure:The distribution of individuals across different age groups.
- Socioeconomic factors:Income, education, and healthcare access can influence fertility, mortality, and migration patterns.
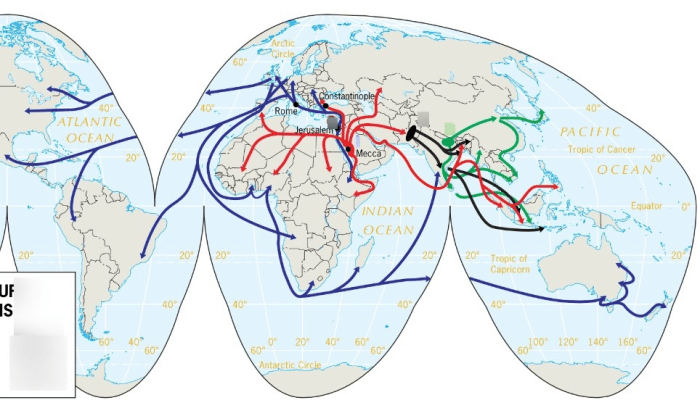
Exploring Migration Patterns
Migration, the movement of people from one place to another, is a complex phenomenon with a long history. In the modern world, migration is often driven by economic, social, political, and environmental factors.
Causes and Consequences of International Migration
International migration is the movement of people across national borders. The causes of international migration are complex and vary from individual to individual. Some of the most common causes include:
- Economic factors: People often migrate to find better economic opportunities, such as higher wages or more job opportunities.
- Social factors: People may also migrate to be closer to family or friends, or to escape persecution or violence.
- Political factors: People may migrate to escape political instability or conflict.
- Environmental factors: People may migrate to escape natural disasters or climate change.
International migration can have a significant impact on both sending and receiving countries. For sending countries, migration can lead to a loss of skilled workers and a decrease in population growth. However, it can also lead to an increase in remittances, which can help to boost the economy.
For receiving countries, migration can lead to an increase in diversity and a boost to the economy. However, it can also lead to social tensions and discrimination.
Causes and Consequences of Internal Migration
Internal migration is the movement of people within a country. The causes of internal migration are similar to the causes of international migration. However, internal migration is often more common than international migration. This is because it is easier and less expensive to move within a country than to move to another country.Internal
migration can have a significant impact on both sending and receiving regions. For sending regions, migration can lead to a loss of skilled workers and a decrease in population growth. However, it can also lead to an increase in remittances, which can help to boost the economy.
For receiving regions, migration can lead to an increase in diversity and a boost to the economy. However, it can also lead to social tensions and discrimination.
The Role of Push and Pull Factors in Migration Decisions
Push factors are factors that encourage people to leave their home country. Pull factors are factors that attract people to a new country. Both push and pull factors can influence migration decisions.Some common push factors include:
- Economic hardship
- Political instability
- Violence
- Natural disasters
- Climate change
Some common pull factors include:
- Economic opportunities
- Political stability
- Safety
- A better climate
- Access to education and healthcare
The decision to migrate is often a difficult one. People must weigh the push and pull factors involved and decide whether the benefits of migration outweigh the costs.
Understanding Urbanization Trends: Aphg Unit 4 Practice Test
Urbanization refers to the process of increasing population density in urban areas, driven by factors such as industrialization, improved transportation, and economic opportunities. Throughout history, urbanization has shaped human societies and continues to be a defining characteristic of contemporary society.
Characteristics and Challenges of Urban Environments
Urban environments are characterized by high population density, complex infrastructure, and a diverse mix of economic activities. However, they also face challenges such as air and water pollution, traffic congestion, and inequality.
Role of Cities in Economic Development and Global Interconnectedness
Cities serve as hubs for economic activity, innovation, and cultural exchange. They attract businesses, investment, and talent, contributing to regional and national economic growth. Additionally, cities play a vital role in global interconnectedness through transportation, communication, and trade.
Creating Tables and Diagrams
Tables and diagrams play a crucial role in presenting population statistics and migration trends in a clear and concise manner.
HTML tables are an effective way to organize and display numerical data, allowing for easy comparison and analysis. Flowcharts and diagrams, on the other hand, help visualize the relationships and patterns within complex demographic information.
Tables, Aphg unit 4 practice test
When creating HTML tables, it’s important to ensure that the data is well-structured and organized. Each row should represent a different data point, while columns represent different categories or variables.
For example, a table showing population statistics could have rows for each country and columns for population size, population density, and growth rate.
Flowcharts and Diagrams
Flowcharts and diagrams are useful for illustrating the movement and flow of population over time and space. They can show the relationships between migration, urbanization, and population change.
For example, a flowchart could be used to show the different stages of the migration process, from the decision to migrate to the arrival at the destination.
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of this practice test?
This practice test is designed to help you assess your understanding of the concepts covered in APHG Unit 4 and prepare you for the actual AP exam.
What topics are covered in this practice test?
This practice test covers all the key concepts from APHG Unit 4, including population, migration, and urbanization.
How can I use this practice test?
You can use this practice test to study for the AP exam, review the material from APHG Unit 4, or simply test your knowledge of population, migration, and urbanization.